Announcing Hurl 4.0.0
The Hurl team is happy to announce Hurl 4.0.0 
Hurl is a command line tool powered by curl, that runs HTTP requests defined in a simple plain text format:
GET https://example.org/api/tests/4567
HTTP 200
[Asserts]
header "x-foo" contains "bar"
certificate "Expire-Date" daysAfterNow > 15
jsonpath "$.status" == "RUNNING" # Check the status code
jsonpath "$.tests" count == 25 # Check the number of items
jsonpath "$.id" matches /\d{4}/ # Check the format of the id
What’s New in This Release
- Improved HTML Report with Request Waterfall
- Detailed Error for CI/CD
- New Filters: decode and xpath
- JSONPath Change
- Custom HTTP Methods
Improved HTML Report with Request Waterfall
We’ve improved Hurl HTML report. The HTML report is pure HTML, without any JavaScript and with inlined CSS, so it’s should be easy to integrate in your favorite CI/CD solution (like GitLab CI/CD or GitHub Actions for instance). Now, each run produces:
- a waterfall timeline: each request/response is displayed on a beautiful graph, with easy access to response timings (DNS,
TCP handshake, time to first byte etc...). These timings are provided by
libcurland you can find an explanation of each indicator in the documentation - a run log with request and response headers, certificate info etc...
- a syntax colored source file with inline errors
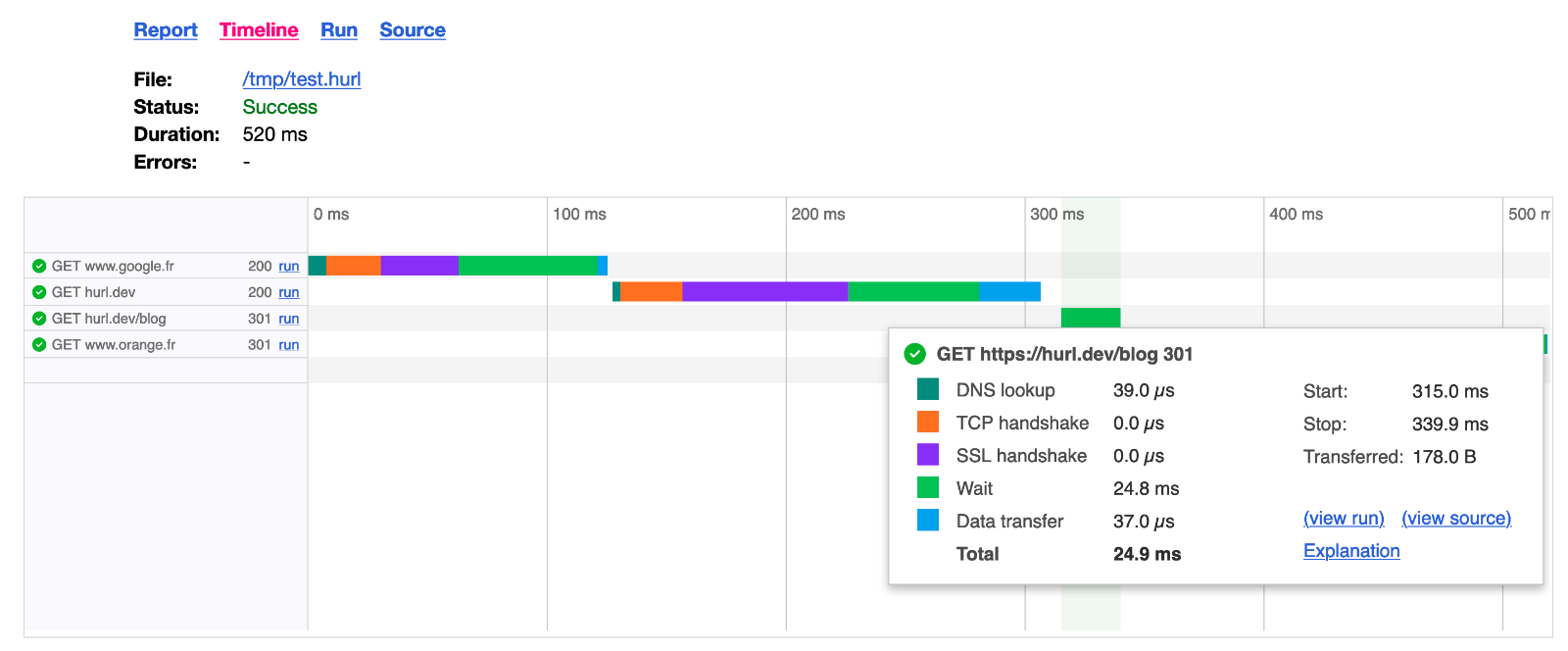
The timings used to construct the requests timeline are also exposed through --json option. --json gives you a structured
view of a Hurl run with errors, asserts, certificates, captures, cookies and so timings. You can even use it to produce your own report!
Once you see it, you can’t unsee it
What’s interesting with rich visualisation is it can reveal hidden or not obvious things. For instance, you can have this kind of gaps on some runs:

After analysis, the gap between requests in this sample test is caused by a huge numbers of assertions on the HTTP response. We have, as of Hurl 4.0.0, a naive
approach of asserts computation: each asserts of the same response is independent, and we parse and recompute every assert from scratch.
Until we see these edge cases, we were very proud of Hurl speed (due to the combination of libcurl and
Rust). Now, we know that we have to improve assert performance for the next release 
Detailed Error for CI/CD
When you’ve error in some test, the analysis can be difficult because you don’t have a lot of information apart of the expected values:
$ hurl --test test.hurl
test.hurl: Running [1/1]
error: Assert failure
--> test.hurl:4:0
|
4 | header "Control-Security-Policy" contains "default-src 'self'"
| actual: none
| expected: contains string <default-src 'self'>
|
test.hurl: Failure (1 request(s) in 128 ms)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Executed files: 1
Succeeded files: 0 (0.0%)
Failed files: 1 (100.0%)
Duration: 130 ms
With the new --error-format option, you can opt in for a longer error description. In this mode, the response header and the response
body are automatically logged:
$ hurl --error-format long --test test.hurl
test.hurl: Running [1/1]
HTTP/2 200
date: Thu, 29 Jun 2023 16:06:58 GMT
content-type: text/html
content-length: 58941
last-modified: Thu, 29 Jun 2023 14:37:22 GMT
etag: "649d9722-e63d"
strict-transport-security: max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains
content-security-policy: default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-eval' 'wasm-unsafe-eval'
x-frame-options: SAMEORIGIN
x-content-type-options: nosniff
accept-ranges: bytes
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<link rel="apple-touch-icon" href="/assets/img/hurl-icon-120.png" />
...
...
...
</body>
</html>
error: Assert failure
--> test.hurl:4:0
|
4 | header "Control-Security-Policy" contains "default-src 'self'"
| actual: none
| expected: contains string <default-src 'self'>
|
test.hurl: Failure (1 request(s) in 146 ms)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Executed files: 1
Succeeded files: 0 (0.0%)
Failed files: 1 (100.0%)
Duration: 148 ms
In this example, we can see that there is actually a Content-Security-Policy whereas we’re querying a Control-Security-Policy
header. The bug is now really simple to solve because the response headers and body are logged.
This option is really useful in CI/CD where you want to have all the available context to debug your session, without re-running your tests. Beware that, as the body response is logged, the log can be really long.
New Filters: decode and xpath
Textual asserts in Hurl work by automatically decoding the response body bytes, based on the Content-Type response header.
That way, if we have a Latin 1 encoded HTML or an UFT-8 encoded HTML we can write the same assert without any encoding concern:
# UTF-8 encoded document:
GET https://example.org/charset/utf8
HTTP 200
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
[Asserts]
body == "<p>café</p>"
# Latin1 encoded document:
GET https://example.org/charset/latin1
HTTP 200
Content-Type: text/html; charset=latin1
[Asserts]
body == "<p>café</p>"
To decode a response from bytes to text, Hurl uses charset hint from Content-Type response header. But sometimes the Content-Type
response header doesn’t specify any encoding. Or the encoding is indicated inside the HTML document through <meta> tag:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv='Content-Type' content='text/html; charset=gb2312'>
</head>
<body>你好世界</body>
</html>
In this case, a decode filter can now be used to explicitly decodes bytes to text and do checks:
GET https://example.com/hello_gb231
HTTP 200
[Asserts]
header "Content-Type" == "text/html"
bytes contains hex,c4e3bac3cac0bde7; # 你好世界 encoded in GB2312
bytes decode "gb2312" xpath "string(//body)" == "你好世界"
As hinted in the previous Hurl snippet, you can now evaluate XPath expression on response part with a xpath filter.
JSONPath Change
In Hurl 4.0.0, we’ve slightly changed the evaluation of JSONPath query. There is no proper specifications for JSONPath. The de-facto one, that Hurl tries to follow as closely as possible, is still https://goessner.net/articles/JsonPath/. There are a few edge cases for which several implementations differ. For instance, standard JSONPath always returns a collection, which most of the time is not meaningful, and harder to test. Some implementations (such as the Java library https://github.com/json-path/JsonPath) also distinguish between node value (definite path) and collection (indefinite path).
Basically, in Hurl 4.0.0, the only selectors returning a value are:
- array index selector (
$.store.book[2]) - object key selector (
$.store.bicycle.color/$.store.bicycle['color'])
Other selectors, that use filters (for instance ?(@.price >= 10) or $[*].id) will return a collection. You can then use
nth filter to extract a value from this collection.
GET https://example.com/books
HTTP 200
[Asserts]
jsonpath "$.store.book[0].title" == "Dune"
jsonpath "$.store.book[*].title" nth 0 == "Dune"
Custom HTTP methods
Hurl 4.0.0 supports now any custom HTTP method. The only constraint is to write the method in uppercase. You can right-away
experiment the incoming new QUERY method:
QUERY https://example.org/contacts
Content-Type: example/query
Accept: text/csv
HTTP 200
Content-Type: text/csv
```
surname, givenname, email
Smith, John, john.smith@example.org
Jones, Sally, sally.jones@example.com
Dubois, Camille, camille.dubois@example.net
```
Others
There are other improvements and bug fixes, you can check a complete list in our release note. If you like Hurl, don’t hesitate to give us a star on GitHub or share it on Twitter!
We’ll be happy to hear from you, either for enhancement requests or for sharing your success story using Hurl!

